Electrodeposition

Electrodeposition is the phase of the electrolytic treatment where the parts are coated with a thin layer (microns) of the metal or alloy that we want to deposit.
To do this, the parts are immersed in an electrolytic solution, called electrolyte, which contains ions of the metal or metals that will form the layer.
A galvanic system is created in which we have an anode, a cathode (the parts to be coated are those that act as a cathode), the electrolyte, where the ions of the metal to be deposited are (Zn, Fe, Ni, …), and a source of direct current that provides electrons, by means of which the reaction of reduction of the metal ions is produced, to be transformed into metal, on the surface of the parts to be coated.
A simple diagram of this galvanic system would be as follows:
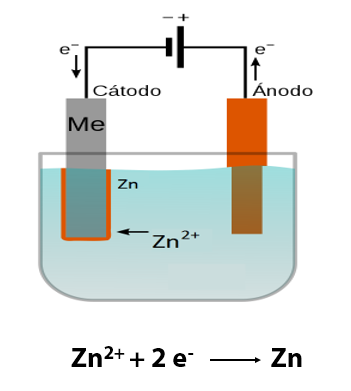
The main factors that influence the correct formation of the coating layer are:
- State of the surface to be coated.
- Composition of the electrolyte.
- Conductivity of the system.
- Applied current density.
- Working temperature of the electrolyte.
- Agitation and filtration of the electrolyte.
All these parameters are controlled at INELCA according to our control plans.


